通过评估不同方法、不同实验室间、模型与观测获得的数据差异以及模型敏感性分析等手段,系统估算出全球大气汞沉降观测和模拟的不确定性分别为±(25-50)%和±(45-70)%,其中干沉降观测与模拟的不确定性最大。GOM和PBM干沉降观测的不确定性来自于目标物种的准确量化,GEM干沉降观测的不确定性则主要源于标准化的实验体系和操作程序的缺乏。GOM和PBM干沉降模拟不确定性较大主要是因为GOM和PBM浓度测量存在较大偏差以及模型参数选择的不确定。
祝贺培生!
Uncertainties in the observation and simulation of global speciated atmospheric Hg deposition to the land surfaces have been systemically estimated based on assessment of commonly used observation methods, campaign results for comparison of different methods, model evaluation with observation data, and sensitivity analysis for model parameterization. The overall uncertainties in the observation and simulation of the total global Hg deposition were estimated to be ± (25–50) % and ± (45–70) %, respectively, with the largest contributions from dry deposition.The uncertainties of GOM and PBM dry deposition measurements come from the interference of unwanted Hg forms or incomplete capture of targeted Hg forms, while that of GEM dry deposition observation originates from the lack of a standardized experimental system and operating procedure. The large biases in the measurements of GOM and PBM concentrations and the high sensitivities of key parameters in resistance models lead to high uncertainties in GOM and PBM dry deposition simulation.
Congratulations to Peisheng!
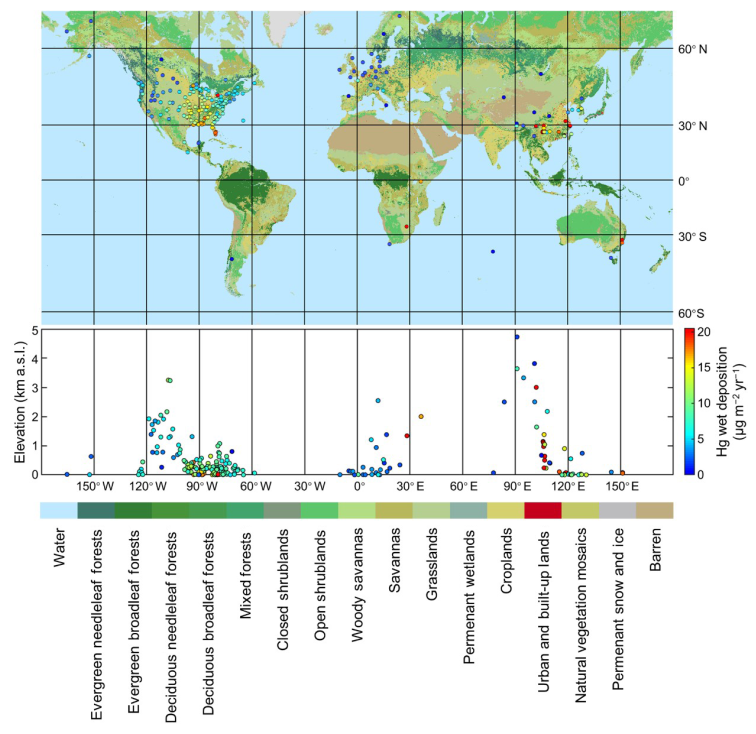
大气汞湿沉降通量全球分布
Global distribution of the observed Hg wet deposition fluxes around the world
Copyright 南京大学赵瑜教授研究组
|苏ICP备10085945号